Introduction
What do your bowel, the incentive in chuck dough, and a developing frog all have in common? Among other effects, they all have cells that carry out mitosis, dividing to produce further cells that are genetically identical to themselves.
Why do these veritably different organisms and apkins all need mitosis? Intestinal cells have to be replaced as they wear out; incentive cells need to reproduce to keep their population growing; and a tadpole must make new cells as it grows bigger and more complex.
What’s mitosis?
Mitosis is a type of cell splitting in which one cell( the mama ) divides to produce two new cells( the daughters) that are intrinsically identical to itself. In the surroundings of the cell cycle, mitosis is the part of the splitting process in which the DNA of the cell’s nexus is resolved into two equal sets of chromosomes.
The great maturity of the cell divisions that be in your body involve mitosis. During development and growth, mitosis populates an organism’s body with cells, and throughout an organism’s life, it replaces old, worn-out cells with new bones . For single- celled eukaryotes like incentive, mitotic divisions are actually a form of reduplication, adding new individualities to the population.
Phases of mitosis
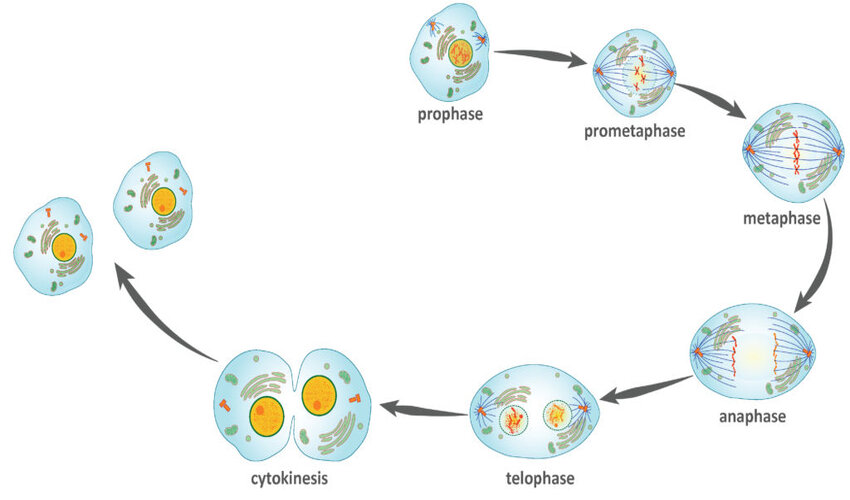
Mitosis consists of four introductory phases prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Some handbooks list five, breaking prophase into an early phase( called prophase) and a late phase( called prometaphase). These phases do in strict successional order, and cytokinesis- the process of dividing the cell contents to make two new cells- thresholds in anaphase or telophase.
Features of Mitosis
- In each cycle of cell division, two son cells are formed from the parent cell.
- The cell is also known as equational cell division because the chromosome number in the parent cell and son cell is the same.
- In shops, mitosis leads to the growth of vegetative corridors of the factory like root tip, stem tip,etc. isolation and combination don’t do in this process.
The processes being during mitosis have been divided into different stages.
Stages of Mitosis
Right before prophase, the cell spends utmost of its life in the interphase, where medications are made before the morning of mitosis( the DNA is copied). still, since the factual process involves the division of the nexus, the prophase is technically the first stage of this process.
The different stages of mitosis being during cell division are given as follows-
Interphase
Before entering mitosis, a cell expend a period of its growth under interphase. It receive the following phases when in interphase
G1 Phase: This is the period before the conflation of DNA.
S Phase: This is the phase during which DNA conflation takes place.
G2 Phase: This is the phase between the end of DNA conflation and the morning of the prophase.
Prophase
Prophase incontinently follows the S and G2 phases of the cycle and is marked by condensation of the inheritable material to form compact mitotic chromosomes composed of two chromatids attached at the centromere.
The completion of the prophase is characterised by the inauguration of the assembly of the mitotic spindle, the microtubules and the proteinaceous factors of the cytoplasm that help in the process.
Prometaphase
In the prometaphase, the nuclear wrapping disintegrates. Now the microtubules are allowed to increase from the centromere to the chromosome. The microtubules join to the kinetochores which permit the cell to shift the chromosome around.
Metaphase
At this stage, the microtubules start to attract the chromosomes with equal enforced and the chromosome ends up in the centre of the cell. This part is known as the metaphase plate. Therefore, each cell gets an entire functioning genome.
Anaphase
The splitting of the family chromatids marks the onset of anaphase. These family chromatids come from the chromosome of the son capitals. The chromosomes are also pulled towards the pole by the fibres attached to the kinetochores of each chromosome.
Telophase
The chromosomes that collect at the two poles start coalescing into an undifferentiated enormous, as the nuclear surround starts forming around it. The nucleolus, Golgi bodies and ER complex, which had faded after prophase started to reappear.
Telophase is followed by cytokinesis, which denotes the division of the cytoplasm to form two son cells. Therefore, it marks the completion of cell division.
Functions of Mitosis
Following are the two important functions of mitosis
Mitosis helps in the development of an organism. In single- celled organisms, mitosis is the process of asexual reduplication.
It helps in the relief of damaged apkins. The cells near the damaged cells begin mitosis when they don’t smell the neighbouring cells. The split cells reach each other and cover the damaged cells.
Significance of Mitosis
- It is responsible for the development of the zygote into a grown-up.
- Equal distribution of chromosomes to each son cell.
- It’s responsible for the growth and development of an existent.
- It maintains the always number of chromosomes in all body cells of an organism.
- It is needed for agamous reduplication, vegetative propagation in shops and is also accountable for the form and rejuvenescence of damaged apkins.
- Mitosis helps in maintaining the chastity of the genome as no recombination or crossing over takes place.
- It’s responsible for the form and rejuvenescence of old and damaged cells in creaturese.g. gut epithelium, blood cells,etc.
Constantly Asked Questions
Q1. Define mitosis.
It is the class of cell splitting by which a single cell divides in such a way as to construct two genetically identical “ son cells ”.
Q2. Why is mitosis called equational division?
It is the process of cell division wherein the chromosomes replicate and get inversely distributed into two son cells. The chromosome number in each son cell is equal to that in the parent cell, i.e., diploid.
Q3. List all the stages of mitosis.
The stages of Mitosis are
Prophase – The chromosomes dock and cake.
Metaphase – Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell.
Anaphase – Chromatids break apart at the centromere and move to contrary poles.
Telophase – Two capitals formed after nuclear envelopes reform around each group of chromosomes.
Q4. What’s prophase?
The process of mitosis begins with the prophase. In this stage, the chromatin condenses and the nucleolus disappears.
Q5. What happens in metaphase?
Metaphase is the alternate stage of the process, chromosomes get condensed at the ambit, before being resolve piecemeal for each of the two son cells.
Q6. In what cells does mitosis do?
It occurs in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells divide by both mitosis and meiosis. Foreg., skin cells divide by mitosis, whereas gametes divide by meiosis.
Q7. What’s the primary function of mitosis?
It plays an important part in the life cycle of utmost living effects. It helps in cell rejuvenescence, asexual reduplication and growth.